Rising Number of Breath Research Publications
Published on: 29 Mar 2019
This blog was initially published in March 2018. We aim to update the content on a regular basis and the most recent update was on 31st March 2025.
Breath analysis, as a field of research, has been around for quite some time. In fact, modern breath testing dates back to 1971, beginning with the groundbreaking work of Nobel Prize winner Linus Pauling. However, recent years have seen a significant increase in the number of publications related to breath analysis, thanks in part to the development of new technologies and the COVID-19 pandemic.
A search for the number of breath analysis publications per year on the Pubmed database visualizes this trend, as shown in Figure 1. There was a notable surge in the number of breath analysis publications in 2021, especially in the context of clinical trials focusing on infectious diseases such as COVID-19. This uplift has now settled back down to pre-COVID levels. However, it is anticipated that publications will pick up again in the coming years, given the potential of breath analysis as a non-invasive diagnostic tool in infectious diseases and other medical fields.
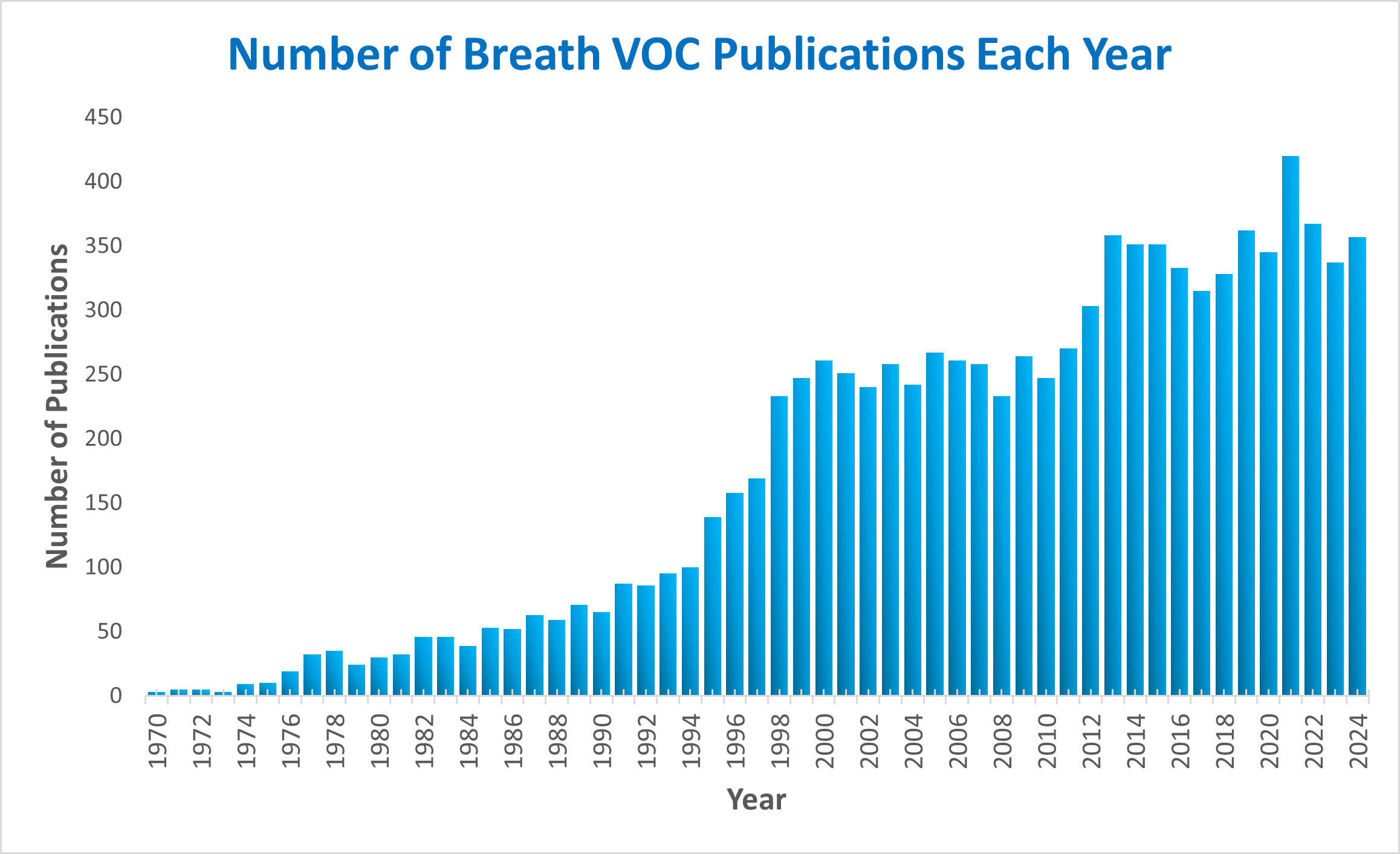
Figure 1. Search made on www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed with searches criteria ((((Breath Analysis[Text Word]) OR Breath Research[Text Word]) OR Breath Biopsy[Text Word]) OR Breath Test[Text Word]) with the date sequenced from March 1970 to March 28th 2025.
Since the start of 2025, there have already been over 100 breath publications. But it’s not just the volume of research that’s increasing – it’s also the range of applications. Figure 2 demonstrates this range, showing the number of publications in the different research areas for 15 months, including 2024 and the first three months of 2025. Breath analysis was once largely limited to a few key areas, such as the Helicobacter pylori breath test using 13C Urea, but now, the use of breath analysis has expanded into broader areas including the development of diagnostic tools and even therapeutics. Currently, breath as analysis is growing as a sampling medium for cancer research, respiratory diseases, liver diseases, endocrine system research as well as the microbiome.
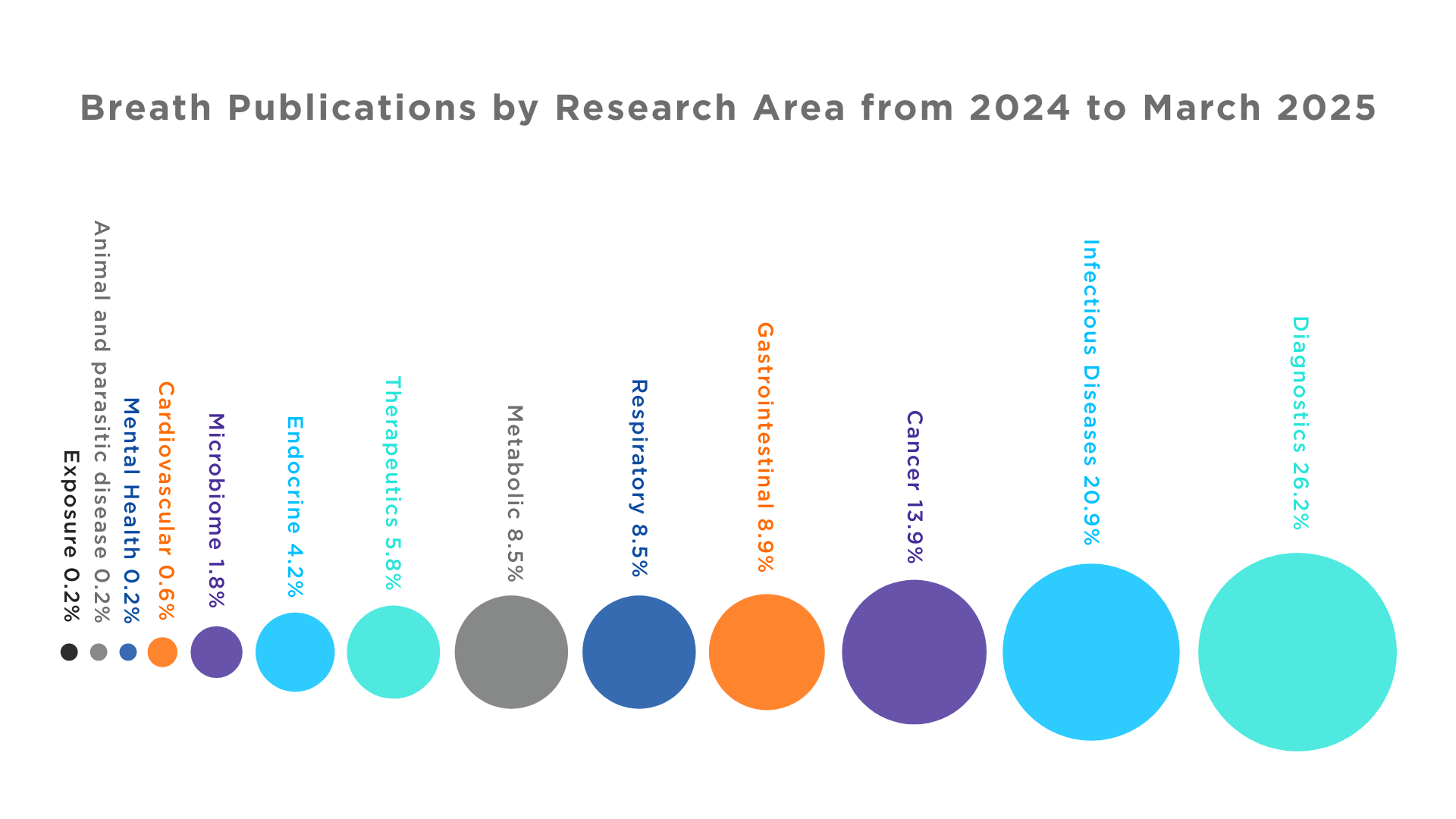
Figure 2. Breath Publications by Research Area from 2024 to March 2025. Data taken from www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed with searches criteria ((((Breath Analysis[Text Word]) OR Breath Research[Text Word]) OR Breath Biopsy[Text Word]) OR Breath Test[Text Word]) in addition to using the major MeSH topic area search function e.g. (… AND (respiratory tract diseases [MeSH Major Topic]))
Owlstone Medical is at the forefront of this research. Our Breath Biopsy® Platform has revolutionized the way in which breath can be utilized in clinical research. By improving the collection, storage, and standardised analysis of breath samples, the Breath Biopsy technology has enabled breath analysis to be included in large-scale clinical trials. This is a game-changer for quantifying biomarkers of processes within the body, as breath analysis has the benefit of being completely non-invasive, making it more patient-friendly than other tests.
Current Research at Owlstone Medical
Breath is a valuable source of potential biomarkers for a wide range of diseases, and other applications. One of our largest trials so far has involved the use of exogenous volatile probes (EVOC) to detect signals coming from even the smallest of tumors to enable the early detection of lung cancer. Having demonstrated that our probe does indeed produce the anticipated response, we have progressed through to the phase 2 clinical trial which assesses the diagnostic performance of the lung cancer test. Other notable work includes Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation funded research on the use of breath biomarkers for infectious diseases such as Malaria and Tuberculosis. Lastly, the gastrointestinal space has recently picked up the pace, with a plethora of gut microbial metabolites being detected. This year, Owlstone Medical’s consumer brand OMED Health will launch the first handheld device that can aid in the diagnosis of digestive conditions. Learn more about the hydrogen-methane detecting breath analyzer for research purposes here.
The desire for a non-invasive test to improve patient experience is one of the driving forces behind the expansion of new application areas for breath research. By enabling earlier and more precise detection of diseases and health conditions, breath analysis can lead to more effective treatments and better outcomes for patients.
In conclusion, breath analysis is a rapidly developing field with significant potential for revolutionizing patient monitoring, and disease diagnosis. With continued advances in technology and research, breath analysis is poised to become an increasingly important tool in the fight against disease.
Breath Biopsy®
If you want to learn more about how Owlstone Medical’s breath sampling and analysis technology and services are being utilized in early detection and precision medicine, why not download our Breath Biopsy Guide? The fourth edition is free to download.
